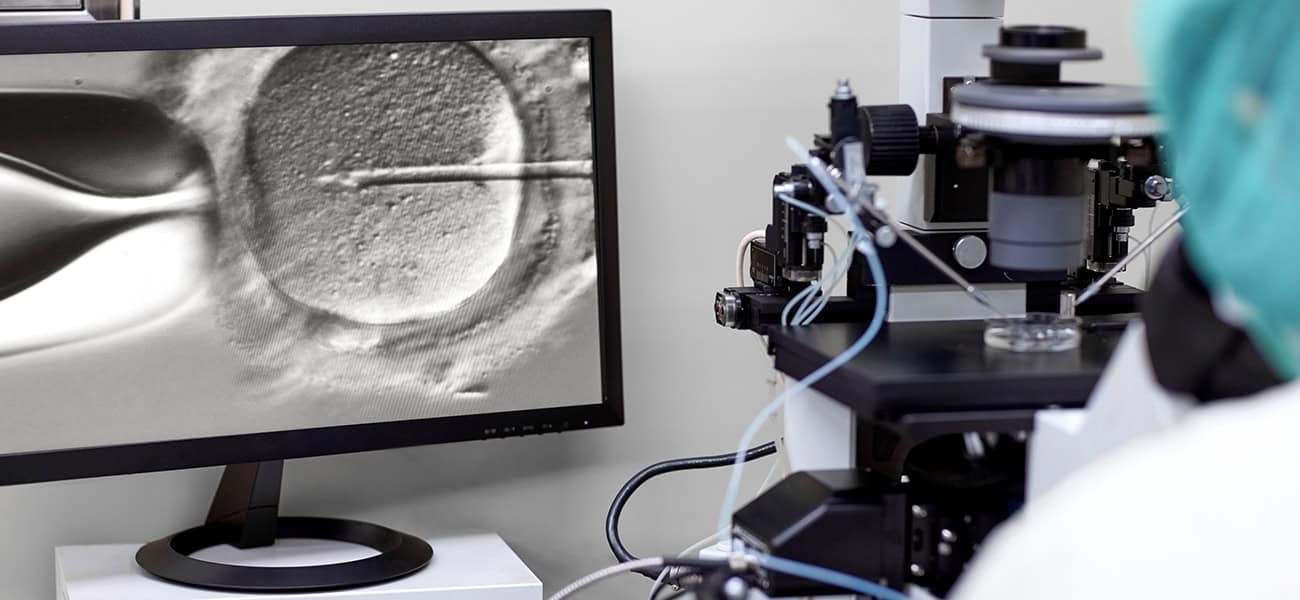
Explainable Artificial Intelligence Transforms Follicle Assessment
A recent study in Nature Communications showcases the integration of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in assessing follicle size—an essential factor influencing IVF success.
Why Follicle Size Matters:
Follicle size plays a critical role in determining fertilization rates and embryo quality. Traditionally, clinicians relied on manual measurements and subjective judgment, which can lead to inconsistencies.
How XAI Improves IVF Outcomes:
- Data-Driven Insights:
The AI model analyzes large datasets to identify follicle sizes most predictive of successful clinical outcomes. - Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency:
By detecting subtle patterns often missed during manual assessments, the model provides more reliable evaluations. - Transparent Decision-Making:
The “explainability” feature ensures clinicians can understand the rationale behind the AI’s conclusions, fostering trust and facilitating its adoption in practice.
Clinical Implications:
- Optimizes ovarian stimulation protocols by identifying ideal follicle sizes.
- Personalizes treatment strategies based on data-driven insights.
- Ultimately improves pregnancy rates by enhancing the precision of clinical decisions.
A Step Forward for Reproductive Medicine:
This study underscores the transformative role of AI in IVF, paving the way for more precise, consistent, and evidence-based patient care
Key Factors Influencing Live Birth Rates in Fresh Embryo Transfers
A recent study published in Scientific Reports provides valuable insights into the factors that influence live birth rates (LBR) in fresh embryo transfer (ET) cycles. By analyzing clinical data from a large cohort of IVF patients, researchers identified critical variables that can help optimize treatment protocols and improve success rates.
Key Findings:
- Maternal Age:
Younger patients exhibited significantly higher LBRs, highlighting age as one of the most influential factors. - Ovarian Reserve:
A higher antral follicle count (AFC) and optimal ovarian response during stimulation correlated with better outcomes. - Embryo Quality:
High-grade blastocysts were strongly associated with increased implantation and live birth rates. - Endometrial Thickness:
An optimal thickness of 8–12 mm was found to maximize the likelihood of successful implantation. - Hormonal Levels During Stimulation:
Balanced estrogen and progesterone levels during ovarian stimulation improved LBRs. - Timing of Trigger Administration & Embryo Transfer:
Precise timing for administering the trigger shot and transferring embryos played a crucial role in enhancing implantation success.
Clinical Implications:
This research underscores the importance of personalized IVF protocols. By tailoring treatment strategies based on these predictive factors, clinicians can improve outcomes for a diverse range of patients.
The findings offer a data-driven framework to help fertility specialists refine their practices, ultimately increasing the chances of achieving successful pregnancies.
Endometriosis Does Not Increase Aneuploidy Rates in IVF Embryos
A recent study in Scientific Reports has shed light on the relationship between endometriosis and aneuploidy rates in IVF embryos—addressing a long-standing question in reproductive medicine.
Understanding the Concern:
Endometriosis, a condition where endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus, is known to impact fertility. However, its potential effect on embryo chromosomal integrity has remained uncertain—until now.
Study Overview:
Researchers analyzed data from IVF cycles of patients with and without endometriosis, comparing aneuploidy rates through preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A).
Key Findings:
- No Significant Difference in Aneuploidy Rates:
Embryos from patients with endometriosis had similar rates of chromosomal abnormalities compared to those without the condition. - Genetic Integrity Remains Intact:
Endometriosis does not inherently increase the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos.
Clinical Implications:
- These results offer reassurance to patients with endometriosis pursuing IVF.
- Fertility specialists can confidently advise that embryo quality, in terms of chromosomal integrity, is not compromised by the presence of endometriosis.
- The study reinforces the importance of focusing on other fertility factors, such as ovarian reserve and embryo development, when treating patients with endometriosis.
This research provides crucial insights for personalized IVF treatment plans, ensuring patients receive accurate, evidence-based information when navigating their fertility journey.
Explainable Artificial Intelligence Transforms Follicle Assessment
A recent study in Nature Communications showcases the integration of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in assessing follicle size—an essential factor influencing IVF success.
Why Follicle Size Matters:
Follicle size plays a critical role in determining fertilization rates and embryo quality. Traditionally, clinicians relied on manual measurements and subjective judgment, which can lead to inconsistencies.
How XAI Improves IVF Outcomes:
- Data-Driven Insights:
The AI model analyzes large datasets to identify follicle sizes most predictive of successful clinical outcomes. - Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency:
By detecting subtle patterns often missed during manual assessments, the model provides more reliable evaluations. - Transparent Decision-Making:
The “explainability” feature ensures clinicians can understand the rationale behind the AI’s conclusions, fostering trust and facilitating its adoption in practice.
Clinical Implications:
- Optimizes ovarian stimulation protocols by identifying ideal follicle sizes.
- Personalizes treatment strategies based on data-driven insights.
- Ultimately improves pregnancy rates by enhancing the precision of clinical decisions.
A Step Forward for Reproductive Medicine:
This study underscores the transformative role of AI in IVF, paving the way for more precise, consistent, and evidence-based patient care
Key Factors Influencing Live Birth Rates in Fresh Embryo Transfers
A recent study published in Scientific Reports provides valuable insights into the factors that influence live birth rates (LBR) in fresh embryo transfer (ET) cycles. By analyzing clinical data from a large cohort of IVF patients, researchers identified critical variables that can help optimize treatment protocols and improve success rates.
Key Findings:
- Maternal Age:
Younger patients exhibited significantly higher LBRs, highlighting age as one of the most influential factors. - Ovarian Reserve:
A higher antral follicle count (AFC) and optimal ovarian response during stimulation correlated with better outcomes. - Embryo Quality:
High-grade blastocysts were strongly associated with increased implantation and live birth rates. - Endometrial Thickness:
An optimal thickness of 8–12 mm was found to maximize the likelihood of successful implantation. - Hormonal Levels During Stimulation:
Balanced estrogen and progesterone levels during ovarian stimulation improved LBRs. - Timing of Trigger Administration & Embryo Transfer:
Precise timing for administering the trigger shot and transferring embryos played a crucial role in enhancing implantation success.
Clinical Implications:
This research underscores the importance of personalized IVF protocols. By tailoring treatment strategies based on these predictive factors, clinicians can improve outcomes for a diverse range of patients.
The findings offer a data-driven framework to help fertility specialists refine their practices, ultimately increasing the chances of achieving successful pregnancies.
Endometriosis Does Not Increase Aneuploidy Rates in IVF Embryos
A recent study in Scientific Reports has shed light on the relationship between endometriosis and aneuploidy rates in IVF embryos—addressing a long-standing question in reproductive medicine.
Understanding the Concern:
Endometriosis, a condition where endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus, is known to impact fertility. However, its potential effect on embryo chromosomal integrity has remained uncertain—until now.
Study Overview:
Researchers analyzed data from IVF cycles of patients with and without endometriosis, comparing aneuploidy rates through preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A).
Key Findings:
- No Significant Difference in Aneuploidy Rates:
Embryos from patients with endometriosis had similar rates of chromosomal abnormalities compared to those without the condition. - Genetic Integrity Remains Intact:
Endometriosis does not inherently increase the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos.
Clinical Implications:
- These results offer reassurance to patients with endometriosis pursuing IVF.
- Fertility specialists can confidently advise that embryo quality, in terms of chromosomal integrity, is not compromised by the presence of endometriosis.
- The study reinforces the importance of focusing on other fertility factors, such as ovarian reserve and embryo development, when treating patients with endometriosis.
This research provides crucial insights for personalized IVF treatment plans, ensuring patients receive accurate, evidence-based information when navigating their fertility journey.
biweekly insights